-
 E-mail
xhcnlite@ytxinhai.com
E-mail
xhcnlite@ytxinhai.com
-
 Call Us
008613641173523
Call Us
008613641173523
 E-mail
xhcnlite@ytxinhai.com
E-mail
xhcnlite@ytxinhai.com
 Call Us
008613641173523
Call Us
008613641173523
2025-12-22 Views: 367
Warm Tip: If you want to know more information, like quotation, products, solutions, etc., please Click here ,and contact us online.

When dealing with the flotation processes of copper-lead-zinc sulfide ores, it is essential to first conduct in-depth research on the composition and structural characteristics of the ores. Based on such information, a suitable flotation separation process flow can be designed. Below is a detailed introduction to the four major copper-lead-zinc flotation processes.
The preferential flotation process is suitable for ores with simple compositions, high raw ore grades, and significant differences in the floatability of useful minerals. The process includes the following steps:
Copper Ore Flotation: Firstly, inhibitors are added to suppress the floatability of lead and zinc minerals. Then, collectors are introduced to promote the combination of copper minerals with air bubbles. Subsequently, frothers are added to stabilize the foam layer, completing the separation of copper concentrate. During operation, it is necessary to control the dosage of reagents, pH value, and temperature.
Lead Ore Flotation: After copper ore flotation, inhibitors are added to the pulp to inhibit the floatation of zinc minerals. Collectors are used to capture lead minerals, and frothers are added to stabilize the foam layer, thus separating lead concentrate. Strict operational control is required to improve recovery rate and concentrate grade.
Zinc Ore Flotation: Copper sulfate is used as an activator to enhance the floatability of zinc minerals. Collectors are then added to capture zinc minerals, followed by the addition of frothers to make them float, separating zinc concentrate. Effective separation is achieved by regulating reagent dosage and flotation cell conditions.
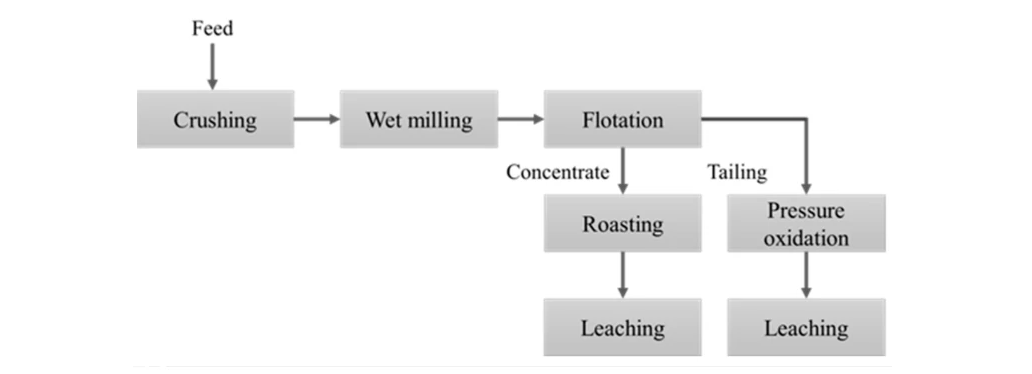
This process is applicable to polymetallic ores where useful minerals are unevenly disseminated, closely intergrown with each other, or one useful mineral is finely disseminated in another, while their aggregates are coarsely disseminated in gangue. The process flow consists of three stages:
Bulk Flotation Stage: Collectors and frothers are added to make copper, lead, and zinc minerals float together to form bulk concentrate, achieving preliminary enrichment.
Regrinding and Reagent Removal of Bulk Concentrate: Reagent films on the mineral surface and excess reagents in the pulp are removed through mechanical reagent removal methods (multiple cleaning, regrinding, thickening, scrubbing, filtration, and washing), desorption methods (using sodium sulfide and activated carbon), and heating methods.
Separation Stage: The pulp pH value and collectors (such as xanthate, butyl xanthate, and dithiophosphate) are adjusted in stages to sequentially realize the floatation and separation of copper, lead, and zinc minerals.
The partial bulk-preferential flotation process is suitable for copper-lead-zinc polymetallic sulfide ores with similar floatability. The process steps are as follows:
Bulk Flotation of Copper and Lead: Lime is used for pulp conditioning to ensure an appropriate pulp pH value. Ty-1 and zinc sulfate are employed as inhibitors, while ethyl xanthate and J-21 serve as collectors. This realizes the effective separation of zinc minerals from copper and lead minerals, ensures moderate foam viscosity, and creates favorable conditions for the subsequent copper-lead separation.
Copper-Lead Separation: The method of inhibiting lead and floating copper is adopted. Ethyl xanthate and No. 2 oil are used as collectors and frothers to obtain high-grade copper concentrate. Subsequently, a gravity separation shaking table is used to improve the grade of lead concentrate. Depending on the mineral type, inhibitors such as cyanides and the oxygen-sulfur method are selected to adjust flotation reagents.
Zinc Flotation from Tailings: Roughing is performed on the tailings from copper-lead bulk flotation. Lime, copper sulfate, butyl xanthate, and No. 2 oil are used to adjust the flotation pH value to obtain high-grade zinc concentrate. Then, two stages of cleaning and one stage of scavenging are carried out to ensure the improvement of zinc concentrate grade.
Following the separation principle of "floating easy-to-float minerals first and then difficult-to-float ones", the recoverable minerals are divided into two parts (easy-to-float and difficult-to-float) according to the differences in their natural floatability. Bulk flotation is conducted separately to obtain bulk concentrates, and then copper, lead, and zinc concentrates are separated sequentially. The process includes three steps:
Bulk Flotation Stage of Easy-to-Float Minerals: The natural floatability of minerals is utilized or collectors are added to enhance the floatability of easy-to-float minerals, and preferential flotation is carried out to form preliminary bulk concentrate.
Bulk Flotation Stage of Difficult-to-Float Minerals: Sulfidizing agents are added and the pH value is adjusted to improve the floatability of difficult-to-float minerals, obtaining bulk concentrate of difficult-to-float minerals.
Separation Stage: Copper sulfate is used to activate copper minerals, xanthate as the collector, and frother to generate foam for flotation, thus obtaining copper concentrate. Inhibitors are added, dithiophosphate as the collector, and frother to produce foam for flotation, thereby obtaining lead concentrate. For zinc concentrate, copper sulfate is used to activate zinc minerals, thiocarbamide collectors to capture zinc minerals, and frother to create foam for flotation. Through these steps, the effective separation of copper, lead, and zinc minerals is achieved sequentially.
Through a comprehensive understanding of the four major copper-lead-zinc flotation processes, we can see that selecting the appropriate flotation process is crucial for improving the recovery rate and grade of ores when processing copper-lead-zinc sulfide ores. Whether it is the preferential flotation, bulk-preferential flotation, partial bulk-preferential flotation, or iso-floatability flotation process, each process has its applicable ore characteristics and operational key points. In actual production, it is necessary to flexibly select and adjust the flotation process flow according to the ore composition, structural characteristics, and changes in process conditions, so as to achieve economic, efficient, and environmentally friendly goals.
No. 188, Xinhai Street, high-tech Industrial Park, Fushan District, Yantai, Shandong, China.

Please leave your message here! We will send detail technical info and quotation to you!